What Is Plantar Fasciitis And Find Out How To Heal It
Overview
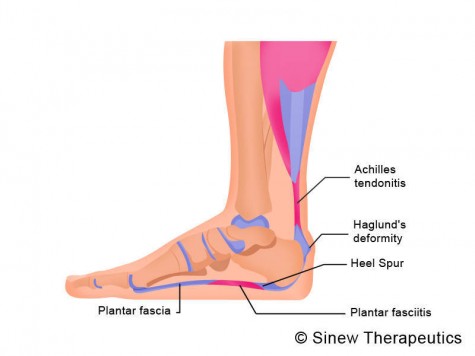
The plantar fascia is a strong, relatively inflexible, fibrous ligament band that runs through the bottom of the foot. That band helps to keep the complex arch system of the foot, absorb shock, plays a role in body balance and in the various phases of gait. The band transmits your weight across the bottom of the foot with each step you take. When the heel of the trailing leg starts to get off the ground, the band bears tension that is approximately twice the body weight. The tension on the band at this moment is even greater if the calf muscles are not flexible enough.
Causes
Inappropriate footwear is the No. 1 cause of plantar fasciosis. Footwear that possesses toe spring and a tapered toe box holds your big toe in an adducted and extended position. In this position, your abductor hallucis muscle-the muscle responsible for moving your big toe away from your foot’s midline-pulls on a foot structure called the flexor retinaculum and may restrict blood flow through your posterior tibial artery, the vessel that carries blood to the bottom of your foot. Tissues in the sole of your feet begin to degenerate as blood supply to this area is decreased. Other recognized causes of or contributors to this health problem include the following, calf muscle shortening, plantar fascia contracture, Obesity, rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis, Psoriatic arthritis, Corticosteroid injections.
Symptoms
The most obvious symptom of plantar fasciitis is a sharp pain on the bottom of the foot, near the heel. Here are some signals that this pain may be plantar fasciitis. The pain is strongest first thing in the morning but gets better after a few minutes of walking around. The pain is worse after standing for a long time or after getting up from sitting. The pain develops gradually and becomes worse over time. The pain is worse after exercise or activity than it is during activity. It hurts when stretching the foot. It hurts when pressing on the sides of the heel or arch of the foot.
Diagnosis
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist is usually sufficient to diagnose plantar fasciitis. Occasionally, further investigations such as an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI may be required to assist with diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
The initial treatment of plantar fasciitis focuses on reducing pain and inflammation. Resting the affected foot is the most important aspect of this treatment. Other initial treatment may include, aplying ice to the sole of the foot, Anti-inflammatory medications. Gentle stretching of the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon. Physiotherapy. Taping the foot and ankle to provide adequate support and alignment, Wearing supportive footwear with shock-absorbing soles or inserts. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Brufen) and diclofenac (Voltaren) are often used to treat plantar fasciitis. It is unclear whether NSAIDs assist in the healing process but they are useful for controlling pain during treatment. If the condition does not respond to initial treatment, a corticosteroid therapy may be recommended. This involves the injection of corticosteroid medication such as hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef) directly into the affected area in order to treat the inflammation and thus relieve the pain. Night splints to prevent the plantar fascia tightening during sleep may also be recommended at this stage.
Surgical Treatment
The most common surgical procedure for plantar fasciitis is plantar fascia release. It involves surgical removal of a part from the plantar fascia ligament which will relieve the inflammation and reduce the tension. Plantar fascia release is either an open surgery or endoscopic surgery (insertion of special surgical instruments through small incisions). While both methods are performed under local anesthesia the open procedure may take more time to recover. Other surgical procedures can be used as well but they are rarely an option. Complications of plantar fasciitis surgery are rare but they are not impossible. All types of plantar fasciitis surgery pose a risk of infection, nerve damage, and anesthesia related complications including systemic toxicity, and persistence or worsening of heel pain.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises for the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia are recommend to relieve pain and aid in the healing process. Sometimes application of athletic tape is recommended. In moderate or severe cases of plantar fasciitis, your doctor may recommend you wearing a night splint, which will stretch the arch of your foot and calf while you sleep. This helps to lengthen the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia for symptom relief. Depending on the severity of your plantar fasciitis, your physician may prescribe a store-bought orthotic (arch support) or custom-fitted orthotic to help distribute your foot pressure more evenly.