Find Out About Overpronation Of The Foot
Overview
Over pronation is when there is excessive or too much movement of the foot. Over pronation is a very common cause of heel pain and general pain throughout the lower extremities. This condition can often be referred to as flat feet and causes you to walk on other parts of your foot, which is what leads to serious heel and foot pain.
Causes
Generally fallen arches are a condition inherited from one or both parents. In addition, age, obesity, and pregnancy cause our arches to collapse. Being in a job that requires long hours of standing and/or walking (e.g. teaching, retail, hospitality, building etc) contributes to this condition, especially when standing on hard surfaces like concrete floors. Last, but not least unsupportive footwear makes our feet roll in more than they should.
Symptoms
Overpronation can lead to injuries and pain in the foot, ankle, knee, or hip. Overpronation puts extra stress on all the bones in the feet. The repeated stress on the knees, shins, thighs, and pelvis puts additional stress on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the lower leg. This can put the knee, hip, and back out of alignment, and it can become very painful.
Diagnosis
If you have flat feet or low arches, chances are you overpronate. Although not always the case, the lower your arches the greater the overpronate. Stand on a hard surface (in front of a mirror if you need to) and look at your feet, flat feet or low arches are easy to spot. If your feet look flatter than a pancake, have a look at your ankles and see if they seem collapsed or straight. If they are, you're overpronating.
Non Surgical Treatment
No matter what the cause in your case, over pronation can be remedied in several ways. Those who are overweight should consider permanently losing weight to naturally alleviate pressure on the ligaments and heel of the foot. Also, you should consult a podiatrist to examine your posture and movement habits. You may be reinjuring yourself due to poor alignment without even knowing it. If you also have lower back problems, this could be a sign of over pronation as a result of misalignment.
Prevention
Many of the prevention methods for overpronation orthotics, for example, can be used interchangeably with treatment methods. If the overpronation is severe, you should seek medical attention from a podiatrist who can cast you for custom-made orthotics. Custom-made orthotics are more expensive, but they last longer and provide support, stability, and balance for the entire foot. You can also talk with a shoe specialist about running shoes that offer extra medial support and firm heel counters. Proper shoes can improve symptoms quickly and prevent them from recurring. Surgery can sometimes help cure and prevent this problem if you suffer from inherited or acquired pes planus deformity. Surgery typically involves stabilizing the bones to improve the foot?s support and function.
Over pronation is when there is excessive or too much movement of the foot. Over pronation is a very common cause of heel pain and general pain throughout the lower extremities. This condition can often be referred to as flat feet and causes you to walk on other parts of your foot, which is what leads to serious heel and foot pain.

Causes
Generally fallen arches are a condition inherited from one or both parents. In addition, age, obesity, and pregnancy cause our arches to collapse. Being in a job that requires long hours of standing and/or walking (e.g. teaching, retail, hospitality, building etc) contributes to this condition, especially when standing on hard surfaces like concrete floors. Last, but not least unsupportive footwear makes our feet roll in more than they should.
Symptoms
Overpronation can lead to injuries and pain in the foot, ankle, knee, or hip. Overpronation puts extra stress on all the bones in the feet. The repeated stress on the knees, shins, thighs, and pelvis puts additional stress on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the lower leg. This can put the knee, hip, and back out of alignment, and it can become very painful.
Diagnosis
If you have flat feet or low arches, chances are you overpronate. Although not always the case, the lower your arches the greater the overpronate. Stand on a hard surface (in front of a mirror if you need to) and look at your feet, flat feet or low arches are easy to spot. If your feet look flatter than a pancake, have a look at your ankles and see if they seem collapsed or straight. If they are, you're overpronating.

Non Surgical Treatment
No matter what the cause in your case, over pronation can be remedied in several ways. Those who are overweight should consider permanently losing weight to naturally alleviate pressure on the ligaments and heel of the foot. Also, you should consult a podiatrist to examine your posture and movement habits. You may be reinjuring yourself due to poor alignment without even knowing it. If you also have lower back problems, this could be a sign of over pronation as a result of misalignment.
Prevention
Many of the prevention methods for overpronation orthotics, for example, can be used interchangeably with treatment methods. If the overpronation is severe, you should seek medical attention from a podiatrist who can cast you for custom-made orthotics. Custom-made orthotics are more expensive, but they last longer and provide support, stability, and balance for the entire foot. You can also talk with a shoe specialist about running shoes that offer extra medial support and firm heel counters. Proper shoes can improve symptoms quickly and prevent them from recurring. Surgery can sometimes help cure and prevent this problem if you suffer from inherited or acquired pes planus deformity. Surgery typically involves stabilizing the bones to improve the foot?s support and function.
Will Severs Disease Often Need To Have Surgical Treatment?
Overview
Sever's disease (calcaneal apophysitis) is a common cause of heel pain, particularly in physically active young people who are about to begin puberty. The cause is uncertain, but it is thought that the long calf bones of the leg grow faster than the surrounding muscle and soft tissue, causing the Achilles tendon to pull uncomfortably tight.
Causes
Inflammation occurs at the insertion of the achilles tendon into the back of the heel due to a number of reasons. One or several of the following may cause the initiation of Sever?s disease. Rapid growth spurt. Tight calf muscles. Change in footwear (soccer boots / athletic shoes no heel). Excessive rolling in of feet. Poor warm up routine. Remember this condition usually settles as the growth plate fuses within 6-12 months.
Symptoms
Sharp pain will be present in the affected heel (or both heels), especially while running or walking. Pain can be heightened following activity. The area will be tender to the touch and usually becomes inflamed or reddened. It may also be painful to press on the heel with a finger from the back or to squeeze the sides together; the latter is particularly common. You might notice stiffness in some of the surrounding muscles, making regular movements more difficult to achieve. This and the pain can manifest physically in abnormal practices like tiptoeing or limping. In some cases a lump can be detected on the back of the heel, though it may be so small as to defy detection.
Diagnosis
Low-grade inflammation of the calcaneal apophysis cannot be seen on x-ray. Therefore, although x-rays are often done to rule out bony injuries in children with Sever's disease these x-rays are usually normal. Advanced Sever's disease can be seen on x-ray but usually the problem is treated before it reaches this point. Other diagnostic tests, such as bone scans or MRI's, are not usually required in typical cases of Sever's disease. These, or other tests, may be required to rule out other conditions, such as stress fractures of the calcaneus or other bony abnormalities that can mimic Severs disease.
Non Surgical Treatment
Resting the foot and applying ice to the affected area are some of the most effective methods when it comes to treating Sever?s Disease. Make sure the ice is always wrapped in a cloth of some sort. Applying ice directly to the skin can cause frostbite. A monitored stretching program of the lower limbs (particularly of the calf muscles) as well as a small heel lift may also be suggested.
Prevention
Treat symptoms when they occur with RICE and NO HARM. RICE (Rest Ice, Compression and Elevation) will help following activity and when symptoms flare, while No HARM (No Heat, alcohol, running or massage) will help reduce the symptoms from occurring. Orthotics. The use of an Interpod Orthotic will assist in realigning the foot, which will reduce the stress on the Achilles Tendon and prevent reoccurring symptoms. The orthotic achieves this by reducing the forces and stress placed on the limbs during walking and running. Exercise reduction. Patients may need to reduce their level of activity if this is seen as a contributing factor. Training errors. Ensue athletes warm up and cool down correctly with stretching activities. Footwear. Sporting and school shoes should have an appropriate heel height to assist in offloading of the Achilles tendon.
Sever's disease (calcaneal apophysitis) is a common cause of heel pain, particularly in physically active young people who are about to begin puberty. The cause is uncertain, but it is thought that the long calf bones of the leg grow faster than the surrounding muscle and soft tissue, causing the Achilles tendon to pull uncomfortably tight.
Causes
Inflammation occurs at the insertion of the achilles tendon into the back of the heel due to a number of reasons. One or several of the following may cause the initiation of Sever?s disease. Rapid growth spurt. Tight calf muscles. Change in footwear (soccer boots / athletic shoes no heel). Excessive rolling in of feet. Poor warm up routine. Remember this condition usually settles as the growth plate fuses within 6-12 months.
Symptoms
Sharp pain will be present in the affected heel (or both heels), especially while running or walking. Pain can be heightened following activity. The area will be tender to the touch and usually becomes inflamed or reddened. It may also be painful to press on the heel with a finger from the back or to squeeze the sides together; the latter is particularly common. You might notice stiffness in some of the surrounding muscles, making regular movements more difficult to achieve. This and the pain can manifest physically in abnormal practices like tiptoeing or limping. In some cases a lump can be detected on the back of the heel, though it may be so small as to defy detection.
Diagnosis
Low-grade inflammation of the calcaneal apophysis cannot be seen on x-ray. Therefore, although x-rays are often done to rule out bony injuries in children with Sever's disease these x-rays are usually normal. Advanced Sever's disease can be seen on x-ray but usually the problem is treated before it reaches this point. Other diagnostic tests, such as bone scans or MRI's, are not usually required in typical cases of Sever's disease. These, or other tests, may be required to rule out other conditions, such as stress fractures of the calcaneus or other bony abnormalities that can mimic Severs disease.
Non Surgical Treatment
Resting the foot and applying ice to the affected area are some of the most effective methods when it comes to treating Sever?s Disease. Make sure the ice is always wrapped in a cloth of some sort. Applying ice directly to the skin can cause frostbite. A monitored stretching program of the lower limbs (particularly of the calf muscles) as well as a small heel lift may also be suggested.
Prevention
Treat symptoms when they occur with RICE and NO HARM. RICE (Rest Ice, Compression and Elevation) will help following activity and when symptoms flare, while No HARM (No Heat, alcohol, running or massage) will help reduce the symptoms from occurring. Orthotics. The use of an Interpod Orthotic will assist in realigning the foot, which will reduce the stress on the Achilles Tendon and prevent reoccurring symptoms. The orthotic achieves this by reducing the forces and stress placed on the limbs during walking and running. Exercise reduction. Patients may need to reduce their level of activity if this is seen as a contributing factor. Training errors. Ensue athletes warm up and cool down correctly with stretching activities. Footwear. Sporting and school shoes should have an appropriate heel height to assist in offloading of the Achilles tendon.
Adult Aquired Flat Feet Treatment And Cause
Overview
Collapsed arches occur in five percent of adults 40 years and older, especially those who are overweight or maintain sedentary lifestyles. At the onset of the condition, adult acquired flatfoot can be controlled with anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, taping, bracing, and orthotics. While most cases of adult-onset flatfoot require surgery, congenital flatfoot is an entirely different condition that is best treated with orthotics in children. Ninety percent of children born with flat feet will be fine with conservative treatment.
Causes
Causes of an adult acquired flatfoot may include Neuropathic foot (Charcot foot) secondary to Diabetes mellitus, Leprosy, Profound peripheral neuritis of any cause. Degenerative changes in the ankle, talonavicular or tarsometatarsal joints, or both, secondary to Inflammatory arthropathy, Osteoarthropathy, Fractures, Acquired flatfoot resulting from loss of the supporting structures of the medial longitudinal arch. Dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon Tear of the spring (calcaneoanvicular) ligament (rare). Tibialis anterior rupture (rare). Painful flatfoot can have other causes, such as tarsal coalition, but as such a patient will not present with a change in the shape of the foot these are not included here.
Symptoms
Patients often experience pain and/or deformity at the ankle or hindfoot. When the posterior tibial tendon does not work properly, a number of changes can occur to the foot and ankle. In the earlier stages, symptoms often include pain and tenderness along the posterior tibial tendon behind the inside of the ankle. As the tendon progressively fails, deformity of the foot and ankle may occur. This deformity can include progressive flattening of the arch, shifting of the heel so that it no longer is aligned underneath the rest of the leg, rotation and deformity of the forefoot, tightening of the heel cord, development of arthritis, and deformity of the ankle joint. At certain stages of this disorder, pain may shift from the inside to the outside aspect of the ankle as the heel shifts outward and structures are pinched laterally.
Diagnosis
First, both feet should be examined with the patient standing and the entire lower extremity visible. The foot should be inspected from above as well as from behind the patient, as valgus angulation of the hindfoot is best appreciated when the foot is viewed from behind. Johnson described the so-called more-toes sign: with more advanced deformity and abduction of the forefoot, more of the lateral toes become visible when the foot is viewed from behind. The single-limb heel-rise test is an excellent determinant of the function of the posterior tibial tendon. The patient is asked to attempt to rise onto the ball of one foot while the other foot is suspended off the floor. Under normal circumstances, the posterior tibial muscle, which inverts and stabilizes the hindfoot, is activated as the patient begins to rise onto the forefoot. The gastrocnemius-soleus muscle group then elevates the calcaneus, and the heel-rise is accomplished. With dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon, however, inversion of the heel is weak, and either the heel remains in valgus or the patient is unable to rise onto the forefoot. If the patient can do a single-limb heel-rise, the limb may be stressed further by asking the patient to perform this maneuver repetitively.
Non surgical Treatment
It is imperative that you seek treatment should you notice any symptoms of a falling arch or PTTD. Due to the progressive nature of this condition, your foot will have a much higher chance of staying strong and healthy with early treatment. When pain first appears, your doctor will evaluate your foot to confirm a flatfoot diagnosis and begin an appropriate treatment plan. This may involve rest, anti-inflammatory medications, shoe modifications, physical therapy, orthotics and a possible boot or brace. When treatment can be applied at the beginning, symptoms can most often be resolved without the need for surgery.

Surgical Treatment
In cases where cast immobilization, orthoses and shoe therapy have failed, surgery is the next alternative. The goal of surgery and non-surgical treatment is to eliminate pain, stop progression of the deformity and improve mobility of the patient. Opinions vary as to the best surgical treatment for adult acquired flatfoot. Procedures commonly used to correct the condition include tendon debridement, tendon transfers, osteotomies (cutting and repositioning of bone) and joint fusions. (See surgical correction of adult acquired flatfoot). Patients with adult acquired flatfoot are advised to discuss thoroughly the benefits vs. risks of all surgical options. Most procedures have long-term recovery mandating that the correct procedure be utilized to give the best long-term benefit. Most flatfoot surgical procedures require six to twelve weeks of cast immobilization. Joint fusion procedures require eight weeks of non-weightbearing on the operated foot - meaning you will be on crutches for two months. The bottom line is, Make sure all of your non-surgical options have been covered before considering surgery. Your primary goals with any treatment are to eliminate pain and improve mobility. In many cases, with the properly designed foot orthosis or ankle brace, these goals can be achieved without surgical intervention.
Collapsed arches occur in five percent of adults 40 years and older, especially those who are overweight or maintain sedentary lifestyles. At the onset of the condition, adult acquired flatfoot can be controlled with anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, taping, bracing, and orthotics. While most cases of adult-onset flatfoot require surgery, congenital flatfoot is an entirely different condition that is best treated with orthotics in children. Ninety percent of children born with flat feet will be fine with conservative treatment.

Causes
Causes of an adult acquired flatfoot may include Neuropathic foot (Charcot foot) secondary to Diabetes mellitus, Leprosy, Profound peripheral neuritis of any cause. Degenerative changes in the ankle, talonavicular or tarsometatarsal joints, or both, secondary to Inflammatory arthropathy, Osteoarthropathy, Fractures, Acquired flatfoot resulting from loss of the supporting structures of the medial longitudinal arch. Dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon Tear of the spring (calcaneoanvicular) ligament (rare). Tibialis anterior rupture (rare). Painful flatfoot can have other causes, such as tarsal coalition, but as such a patient will not present with a change in the shape of the foot these are not included here.
Symptoms
Patients often experience pain and/or deformity at the ankle or hindfoot. When the posterior tibial tendon does not work properly, a number of changes can occur to the foot and ankle. In the earlier stages, symptoms often include pain and tenderness along the posterior tibial tendon behind the inside of the ankle. As the tendon progressively fails, deformity of the foot and ankle may occur. This deformity can include progressive flattening of the arch, shifting of the heel so that it no longer is aligned underneath the rest of the leg, rotation and deformity of the forefoot, tightening of the heel cord, development of arthritis, and deformity of the ankle joint. At certain stages of this disorder, pain may shift from the inside to the outside aspect of the ankle as the heel shifts outward and structures are pinched laterally.
Diagnosis
First, both feet should be examined with the patient standing and the entire lower extremity visible. The foot should be inspected from above as well as from behind the patient, as valgus angulation of the hindfoot is best appreciated when the foot is viewed from behind. Johnson described the so-called more-toes sign: with more advanced deformity and abduction of the forefoot, more of the lateral toes become visible when the foot is viewed from behind. The single-limb heel-rise test is an excellent determinant of the function of the posterior tibial tendon. The patient is asked to attempt to rise onto the ball of one foot while the other foot is suspended off the floor. Under normal circumstances, the posterior tibial muscle, which inverts and stabilizes the hindfoot, is activated as the patient begins to rise onto the forefoot. The gastrocnemius-soleus muscle group then elevates the calcaneus, and the heel-rise is accomplished. With dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon, however, inversion of the heel is weak, and either the heel remains in valgus or the patient is unable to rise onto the forefoot. If the patient can do a single-limb heel-rise, the limb may be stressed further by asking the patient to perform this maneuver repetitively.
Non surgical Treatment
It is imperative that you seek treatment should you notice any symptoms of a falling arch or PTTD. Due to the progressive nature of this condition, your foot will have a much higher chance of staying strong and healthy with early treatment. When pain first appears, your doctor will evaluate your foot to confirm a flatfoot diagnosis and begin an appropriate treatment plan. This may involve rest, anti-inflammatory medications, shoe modifications, physical therapy, orthotics and a possible boot or brace. When treatment can be applied at the beginning, symptoms can most often be resolved without the need for surgery.

Surgical Treatment
In cases where cast immobilization, orthoses and shoe therapy have failed, surgery is the next alternative. The goal of surgery and non-surgical treatment is to eliminate pain, stop progression of the deformity and improve mobility of the patient. Opinions vary as to the best surgical treatment for adult acquired flatfoot. Procedures commonly used to correct the condition include tendon debridement, tendon transfers, osteotomies (cutting and repositioning of bone) and joint fusions. (See surgical correction of adult acquired flatfoot). Patients with adult acquired flatfoot are advised to discuss thoroughly the benefits vs. risks of all surgical options. Most procedures have long-term recovery mandating that the correct procedure be utilized to give the best long-term benefit. Most flatfoot surgical procedures require six to twelve weeks of cast immobilization. Joint fusion procedures require eight weeks of non-weightbearing on the operated foot - meaning you will be on crutches for two months. The bottom line is, Make sure all of your non-surgical options have been covered before considering surgery. Your primary goals with any treatment are to eliminate pain and improve mobility. In many cases, with the properly designed foot orthosis or ankle brace, these goals can be achieved without surgical intervention.
The Leading Causes And Solutions For Achilles Tendon Pain
Overview
 A tendon is a tough yet flexible band of fibrous tissue. The tendon is the structure in your body that connects your muscles to the bones. The skeletal muscles in your body are responsible for moving your bones, thus enabling you to walk, jump, lift, and move in many ways. When a muscle contracts it pulls on a bone to cause movements. The structure that transmits the force of the muscle contraction to the bone is called a tendon. Tendons come in many shapes and sizes. Some are very small, like the ones that cause movements of your fingers, and some are much larger, such as your Achilles tendon in your heel. When functioning normally, these tendons glide easily and smoothly as the muscle contracts. Sometimes the tendons become inflamed for a variety of reasons, and the action of pulling the muscle becomes irritating. If the normal smooth gliding motion of your tendon is impaired, the tendon will become inflamed and movement will become painful. This is called tendonitis, and literally means inflammation of the tendon.
A tendon is a tough yet flexible band of fibrous tissue. The tendon is the structure in your body that connects your muscles to the bones. The skeletal muscles in your body are responsible for moving your bones, thus enabling you to walk, jump, lift, and move in many ways. When a muscle contracts it pulls on a bone to cause movements. The structure that transmits the force of the muscle contraction to the bone is called a tendon. Tendons come in many shapes and sizes. Some are very small, like the ones that cause movements of your fingers, and some are much larger, such as your Achilles tendon in your heel. When functioning normally, these tendons glide easily and smoothly as the muscle contracts. Sometimes the tendons become inflamed for a variety of reasons, and the action of pulling the muscle becomes irritating. If the normal smooth gliding motion of your tendon is impaired, the tendon will become inflamed and movement will become painful. This is called tendonitis, and literally means inflammation of the tendon.
Causes
Like any muscle or tendon in the body, the older we get, the more likely we are to sustain an injury. So middle-aged men and women are most at risk, with a slightly higher risk factor attributed to males. Those who participate in more intense athletic activities like high impact sports (tennis, running, basketball) are most susceptible to the injury. Certain underlying medical conditions can also be a contributing factor. Diabetics are more at risk of suffering from Achilles Tendinitis, as are those who are not in great physical shape. Some antibiotics, particularly fluoroquinolones can make one more likely to suffer a strained Achilles Tendon.
Symptoms
Pain anywhere along the tendon, but most often on or close to the heel. Swelling of the skin over the tendon, associated with warmth, redness and tenderness. Pain on rising up on the toes and pain with pushing off on the toes. If you are unable to stand on your toes you may have ruptured the tendon. This requires urgent medical attention. A painful heel for the first few minutes of walking after waking up in the morning. Stiffness of the ankle, which often improves with mild activity.
Diagnosis
Physicians usually pinch your Achilles tendon with their fingers to test for swelling and pain. If the tendon itself is inflamed, your physician may be able to feel warmth and swelling around the tissue, or, in chronic cases, lumps of scar tissue. You will probably be asked to walk around the exam room so your physician can examine your stride. To check for complete rupture of the tendon, your physician may perform the Thompson test. Your physician squeezes your calf; if your Achilles is not torn, the foot will point downward. If your Achilles is torn, the foot will remain in the same position. Should your physician require a closer look, these imaging tests may be performed. X-rays taken from different angles may be used to rule out other problems, such as ankle fractures. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses magnetic waves to create pictures of your ankle that let physicians more clearly look at the tendons surrounding your ankle joint.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The recommended treatment for Achilles tendinitis consists of icing, gentle stretching, and modifying or limiting activity. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or aspirin, can reduce pain and swelling. Physical therapy and the use of an orthotic (heel lift) can also be helpful. For chronic cases where tendinosis is evident and other methods of treatment have failed, surgery may be recommended to remove and repair the damaged tissue.

Surgical Treatment
When the tendon tears or ruptures the variety of surgical techniques are available to repair the damage and restore the tendons function. Recent research that is done at Emory University Department of orthopedics have perfected the repair of the Achilles tendon. The procedure is generally involves making an incision in the back of your leg and stitching the torn tendon together using a technique developed and tested by Dr. Labib. Depending on the condition of the torn tissue the repair may be reinforced with other tendons.
Prevention
Regardless of whether the Achilles injury is insertional or non-insertional, a great method for lessening stress on the Achilles tendon is flexor digitorum longus exercises. This muscle, which originates along the back of the leg and attaches to the tips of the toes, lies deep to the Achilles. It works synergistically with the soleus muscle to decelerate the forward motion of the leg before the heel leaves the ground during propulsion. This significantly lessens strain on the Achilles tendon as it decelerates elongation of the tendon. Many foot surgeons are aware of the connection between flexor digitorum longus and the Achilles tendon-surgical lengthening of the Achilles (which is done to treat certain congenital problems) almost always results in developing hammer toes as flexor digitorum longus attempts to do the job of the recently lengthened tendon. Finally, avoid having cortisone injected into either the bursa or tendon-doing so weakens the tendon as it shifts production of collagen from type one to type three. In a recent study published in the Journal of Bone Joint Surgery(9), cortisone was shown to lower the stress necessary to rupture the Achilles tendon, and was particularly dangerous when done on both sides, as it produced a systemic effect that further weakened the tendon.
 A tendon is a tough yet flexible band of fibrous tissue. The tendon is the structure in your body that connects your muscles to the bones. The skeletal muscles in your body are responsible for moving your bones, thus enabling you to walk, jump, lift, and move in many ways. When a muscle contracts it pulls on a bone to cause movements. The structure that transmits the force of the muscle contraction to the bone is called a tendon. Tendons come in many shapes and sizes. Some are very small, like the ones that cause movements of your fingers, and some are much larger, such as your Achilles tendon in your heel. When functioning normally, these tendons glide easily and smoothly as the muscle contracts. Sometimes the tendons become inflamed for a variety of reasons, and the action of pulling the muscle becomes irritating. If the normal smooth gliding motion of your tendon is impaired, the tendon will become inflamed and movement will become painful. This is called tendonitis, and literally means inflammation of the tendon.
A tendon is a tough yet flexible band of fibrous tissue. The tendon is the structure in your body that connects your muscles to the bones. The skeletal muscles in your body are responsible for moving your bones, thus enabling you to walk, jump, lift, and move in many ways. When a muscle contracts it pulls on a bone to cause movements. The structure that transmits the force of the muscle contraction to the bone is called a tendon. Tendons come in many shapes and sizes. Some are very small, like the ones that cause movements of your fingers, and some are much larger, such as your Achilles tendon in your heel. When functioning normally, these tendons glide easily and smoothly as the muscle contracts. Sometimes the tendons become inflamed for a variety of reasons, and the action of pulling the muscle becomes irritating. If the normal smooth gliding motion of your tendon is impaired, the tendon will become inflamed and movement will become painful. This is called tendonitis, and literally means inflammation of the tendon.
Causes
Like any muscle or tendon in the body, the older we get, the more likely we are to sustain an injury. So middle-aged men and women are most at risk, with a slightly higher risk factor attributed to males. Those who participate in more intense athletic activities like high impact sports (tennis, running, basketball) are most susceptible to the injury. Certain underlying medical conditions can also be a contributing factor. Diabetics are more at risk of suffering from Achilles Tendinitis, as are those who are not in great physical shape. Some antibiotics, particularly fluoroquinolones can make one more likely to suffer a strained Achilles Tendon.
Symptoms
Pain anywhere along the tendon, but most often on or close to the heel. Swelling of the skin over the tendon, associated with warmth, redness and tenderness. Pain on rising up on the toes and pain with pushing off on the toes. If you are unable to stand on your toes you may have ruptured the tendon. This requires urgent medical attention. A painful heel for the first few minutes of walking after waking up in the morning. Stiffness of the ankle, which often improves with mild activity.
Diagnosis
Physicians usually pinch your Achilles tendon with their fingers to test for swelling and pain. If the tendon itself is inflamed, your physician may be able to feel warmth and swelling around the tissue, or, in chronic cases, lumps of scar tissue. You will probably be asked to walk around the exam room so your physician can examine your stride. To check for complete rupture of the tendon, your physician may perform the Thompson test. Your physician squeezes your calf; if your Achilles is not torn, the foot will point downward. If your Achilles is torn, the foot will remain in the same position. Should your physician require a closer look, these imaging tests may be performed. X-rays taken from different angles may be used to rule out other problems, such as ankle fractures. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses magnetic waves to create pictures of your ankle that let physicians more clearly look at the tendons surrounding your ankle joint.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The recommended treatment for Achilles tendinitis consists of icing, gentle stretching, and modifying or limiting activity. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or aspirin, can reduce pain and swelling. Physical therapy and the use of an orthotic (heel lift) can also be helpful. For chronic cases where tendinosis is evident and other methods of treatment have failed, surgery may be recommended to remove and repair the damaged tissue.

Surgical Treatment
When the tendon tears or ruptures the variety of surgical techniques are available to repair the damage and restore the tendons function. Recent research that is done at Emory University Department of orthopedics have perfected the repair of the Achilles tendon. The procedure is generally involves making an incision in the back of your leg and stitching the torn tendon together using a technique developed and tested by Dr. Labib. Depending on the condition of the torn tissue the repair may be reinforced with other tendons.
Prevention
Regardless of whether the Achilles injury is insertional or non-insertional, a great method for lessening stress on the Achilles tendon is flexor digitorum longus exercises. This muscle, which originates along the back of the leg and attaches to the tips of the toes, lies deep to the Achilles. It works synergistically with the soleus muscle to decelerate the forward motion of the leg before the heel leaves the ground during propulsion. This significantly lessens strain on the Achilles tendon as it decelerates elongation of the tendon. Many foot surgeons are aware of the connection between flexor digitorum longus and the Achilles tendon-surgical lengthening of the Achilles (which is done to treat certain congenital problems) almost always results in developing hammer toes as flexor digitorum longus attempts to do the job of the recently lengthened tendon. Finally, avoid having cortisone injected into either the bursa or tendon-doing so weakens the tendon as it shifts production of collagen from type one to type three. In a recent study published in the Journal of Bone Joint Surgery(9), cortisone was shown to lower the stress necessary to rupture the Achilles tendon, and was particularly dangerous when done on both sides, as it produced a systemic effect that further weakened the tendon.
What Causes Heel Discomfort
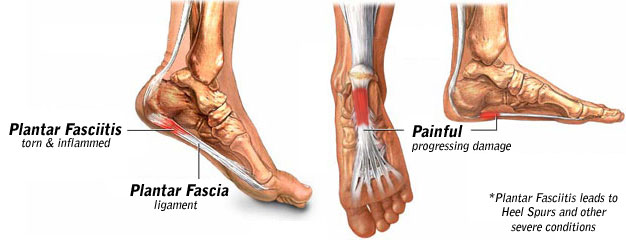
Overview
Plantar Fasciitis is a chronic pain in the heel that can just appear from nowhere but it is actually a long standing mechanical condition caused by prolonged stress on your foot. In most cases Plantar Fasciitis is a common, but very treatable, mechanical condition of the foot and responds positively to orthotics. A heel pain caused by prolonged stress on a ligament like structure in the arch that is very important in weigh-bearing activities. The tissue becomes damaged and needs to be helped to repair in order for the pain to go or subside to a manageable level. Orthotics for your feet can achieve this necessary healing for pain relief. It can be very painful, and even debilitating for sufferers.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis tends to strike those who overtrain, neglect to stretch their calf muscles, or overdo hill work and speedwork. Plantar fasciitis can also be caused by biomechanical flaws, including flat, high-arched feet and a tight Achilles tendon; excessive pronation; sudden increases in training mileage; beginning speedwork; wearing worn running shoes; running on hard surfaces, like asphalt or concrete; or wearing high heels all day before switching into flat running shoes.
Symptoms
The main symptom of plantar fasciitis is heel pain when you walk. You may also feel pain when you stand and possibly even when you are resting. This pain typically occurs first thing in the morning after you get out of bed, when your foot is placed flat on the floor. The pain occurs because you are stretching the plantar fascia. The pain usually lessens with more walking, but you may have it again after periods of rest. You may feel no pain when you are sleeping because the position of your feet during rest allows the fascia to shorten and relax.
Diagnosis
Your doctor may look at your feet and watch the way you stand, walk and exercise. He can also ask you questions about your health history, including illnesses and injuries that you had in your past. The symptoms you have such as the pain location or when does your foot hurts most. Your activity routine such as your job, exercise habits and physical activities preformed. Your doctor may decide to use an X-ray of your foot to detect bones problems. MRI or ultrasound can also be used as further investigation of the foot condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
Cortisone is a powerful anti-inflammatory and when injected directly into the heel it will work almost immediately. Bear in mind however, that the treatment does not address the root cause of the inflammation, and needs to be repeated every few months. Also note, these injections are quite painful, and most doctors today will consider other, less invasive treatment options first. ESWT (Extra Corporeal Shockwave Treatment). A specialist targets therapeutic shockwaves to the affected heel area. This will stimulate a healing response in the affected tissue and ligaments, resulting in reduced inflammation and pain. This treatment and may take from 3 to 4 months to be fully effective. Extracorpreal Shock Wave Therapy is the latest technology to treat chronic plantar fasciitis. It is a non-invasive treatment and highly recommended for people who have tried other treatment like cortisone-injections, accupuncture etc with little or no success. Electroacupuncture and standard acupuncture are used in the treatment of plantar fasciitis and other foot problems such as neuromas and nerve impingement, numbness in the toes etc. In some cases there is nerve entrapment within the foot combined with referred pain from other areas of the body. Some research suggests that acunpuncture can be effective in the treatment of heel pain. A trigger point is an irritable knot in the muscle tissue. When pressed trigger points are very tender and can cause pain in that specific spot or elsewhere in the body (referred pain). The response to pushing into the knot is a muscle twitch. The foot contains 126 muscles, tendons and ligaments, so there are plenty of 'hiding places' for trigger points. Trigger points in the calf muscles often refer pain directly to the bottom of the foot. Trigger point therapy of the lower leg and foot can therefore be successful in the treatment of plantar fasciitis.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is usually not needed for plantar fasciitis. About 95 out of 100 people who have plantar fasciitis are able to relieve heel pain without surgery. Your doctor may consider surgery if non-surgical treatment has not helped and heel pain is restricting your daily activities. Some doctors feel that you should try non-surgical treatment for at least 6 months before you consider surgery. The main types of surgery for plantar fasciitis are Plantar fascia release. This procedure involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament . This releases the tension on the ligament and relieves inflammation . Other procedures, such as removing a heel spur or stretching or loosening specific foot nerves. These surgeries are usually done in combination with plantar fascia release when there is lasting heel pain and another heel problem. Experts in the past thought that heel spurs caused plantar fasciitis. Now experts generally believe that heel spurs are the result, not the cause, of plantar fasciitis. Many people with large heel spurs never have heel pain or plantar fasciitis. So surgery to remove heel spurs is rarely done.
What May Cause Pain Of The Heel And How To End It

Overview
If you experience sharp, throbbing or aching heel pain with your first steps out of bed each morning, or when walking throughout the day, you may be suffering from Plantar Fasciitis. This guide will help you to understand the definition, symptoms and causes of this condition and will explore your treatment options for rapid relief from your pain.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis tends to strike those who overtrain, neglect to stretch their calf muscles, or overdo hill work and speedwork. Plantar fasciitis can also be caused by biomechanical flaws, including flat, high-arched feet and a tight Achilles tendon; excessive pronation; sudden increases in training mileage; beginning speedwork; wearing worn running shoes; running on hard surfaces, like asphalt or concrete; or wearing high heels all day before switching into flat running shoes.
Symptoms
Symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain in the heel of the foot. Some people complain of a sharp stabbing pain especially with walking. Others describe the pain as a dull ache after prolonged standing. The pain of plantar fasciitis is often worst in the morning or following activity.
Diagnosis
Plantar fasciosis is confirmed if firm thumb pressure applied to the calcaneus when the foot is dorsiflexed elicits pain. Fascial pain along the plantar medial border of the fascia may also be present. If findings are equivocal, demonstration of a heel spur on x-ray may support the diagnosis; however, absence does not rule out the diagnosis, and visible spurs are not generally the cause of symptoms. Also, infrequently, calcaneal spurs appear ill defined on x-ray, exhibiting fluffy new bone formation, suggesting spondyloarthropathy (eg, ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis. If an acute fascial tear is suspected, MRI is done.
Non Surgical Treatment
About 90% of plantar fasciitis cases are self-limited and will improve within six months with conservative treatment and within a year regardless of treatment. Many treatments have been proposed for the treatment of plantar fasciitis. First-line conservative approaches include rest, heat, ice, calf-strengthening exercises, techniques to stretch the calf muscles, achilles tendon, and plantar fascia, weight reduction in the overweight or obese, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. NSAIDs are commonly used to treat plantar fasciitis, but fail to resolve the pain in 20% of people. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is an effective treatment modality for plantar fasciitis pain unresponsive to conservative nonsurgical measures for at least three months. Corticosteroid injections are sometimes used for cases of plantar fasciitis refractory to more conservative measures. The injections may be an effective modality for short-term pain relief up to one month, but studies failed to show effective pain relief after three months. Notable risks of corticosteroid injections for plantar fasciitis include plantar fascia rupture, skin infection, nerve or muscle injury, or atrophy of the plantar fat pad. Custom orthotic devices have been demonstrated as an effective method to reduce plantar fasciitis pain for up to 12 weeks. Night splints for 1-3 months are used to relieve plantar fasciitis pain that has persisted for six months. The night splints are designed to position and maintain the ankle in a neutral position thereby passively stretching the calf and plantar fascia overnight during sleep. Other treatment approaches may include supportive footwear, arch taping, and physical therapy.

Surgical Treatment
More invasive procedures to treat plantar fasciitis are usually sought only after other treatment has failed to produce favorable results. Corticosteroid injections deliver medicine into the injured fascia to reduce pain. However, this treatment may weaken the plantar fascia and result in further damage. In addition, extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is a treatment where sound waves are sent through the damaged tissue in order to stimulate the damaged tissue and encourage healing. This method is relatively new in treating plantar fasciitis and your doctor will be able to tell you if it is the right method for you. Lastly, surgery is the last option for those suffering from chronic or severe plantar fasciitis.
Prevention
It is not always possible to prevent heel pain, but there are measures you can take to help avoid further episodes. Healthy weight. Being overweight can place excess pressure and strain on your feet, particularly on your heels. This increases the risk of damaging your feet and heels. If you are overweight, losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight by combining regular exercise with a healthy, balanced diet can be beneficial for your feet. You can calculate your body mass index (BMI) to find out whether you are a healthy weight for your height and build. To work out your BMI, divide your weight in kilograms by your height in metres squared. A BMI of less than 18.5 means that you are underweight, 18.5-24.9 means that your weight is healthy, 25-29 means that you are overweight, 30-40 means that you are obese, over 40 means that you are morbidly obese. You can also use the BMI healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI. Healthy feet. You should always wear footwear that is appropriate for your environment and day-to-day activities. Wearing high heels when you go out in the evening is unlikely to be harmful. However, wearing them all week at work may damage your feet, particularly if your job involves a lot of walking or standing. Ideally, you should wear shoes with laces and a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels.
What Is Plantar Fasciitis And Find Out How To Heal It
Overview
The plantar fascia is a strong, relatively inflexible, fibrous ligament band that runs through the bottom of the foot. That band helps to keep the complex arch system of the foot, absorb shock, plays a role in body balance and in the various phases of gait. The band transmits your weight across the bottom of the foot with each step you take. When the heel of the trailing leg starts to get off the ground, the band bears tension that is approximately twice the body weight. The tension on the band at this moment is even greater if the calf muscles are not flexible enough.
Causes
Inappropriate footwear is the No. 1 cause of plantar fasciosis. Footwear that possesses toe spring and a tapered toe box holds your big toe in an adducted and extended position. In this position, your abductor hallucis muscle-the muscle responsible for moving your big toe away from your foot’s midline-pulls on a foot structure called the flexor retinaculum and may restrict blood flow through your posterior tibial artery, the vessel that carries blood to the bottom of your foot. Tissues in the sole of your feet begin to degenerate as blood supply to this area is decreased. Other recognized causes of or contributors to this health problem include the following, calf muscle shortening, plantar fascia contracture, Obesity, rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis, Psoriatic arthritis, Corticosteroid injections.
Symptoms
The most obvious symptom of plantar fasciitis is a sharp pain on the bottom of the foot, near the heel. Here are some signals that this pain may be plantar fasciitis. The pain is strongest first thing in the morning but gets better after a few minutes of walking around. The pain is worse after standing for a long time or after getting up from sitting. The pain develops gradually and becomes worse over time. The pain is worse after exercise or activity than it is during activity. It hurts when stretching the foot. It hurts when pressing on the sides of the heel or arch of the foot.
Diagnosis
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist is usually sufficient to diagnose plantar fasciitis. Occasionally, further investigations such as an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI may be required to assist with diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
The initial treatment of plantar fasciitis focuses on reducing pain and inflammation. Resting the affected foot is the most important aspect of this treatment. Other initial treatment may include, aplying ice to the sole of the foot, Anti-inflammatory medications. Gentle stretching of the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon. Physiotherapy. Taping the foot and ankle to provide adequate support and alignment, Wearing supportive footwear with shock-absorbing soles or inserts. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Brufen) and diclofenac (Voltaren) are often used to treat plantar fasciitis. It is unclear whether NSAIDs assist in the healing process but they are useful for controlling pain during treatment. If the condition does not respond to initial treatment, a corticosteroid therapy may be recommended. This involves the injection of corticosteroid medication such as hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef) directly into the affected area in order to treat the inflammation and thus relieve the pain. Night splints to prevent the plantar fascia tightening during sleep may also be recommended at this stage.
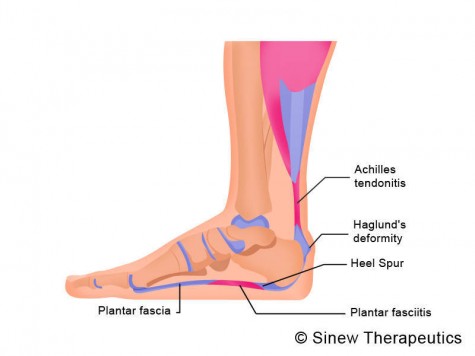
Surgical Treatment
The most common surgical procedure for plantar fasciitis is plantar fascia release. It involves surgical removal of a part from the plantar fascia ligament which will relieve the inflammation and reduce the tension. Plantar fascia release is either an open surgery or endoscopic surgery (insertion of special surgical instruments through small incisions). While both methods are performed under local anesthesia the open procedure may take more time to recover. Other surgical procedures can be used as well but they are rarely an option. Complications of plantar fasciitis surgery are rare but they are not impossible. All types of plantar fasciitis surgery pose a risk of infection, nerve damage, and anesthesia related complications including systemic toxicity, and persistence or worsening of heel pain.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises for the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia are recommend to relieve pain and aid in the healing process. Sometimes application of athletic tape is recommended. In moderate or severe cases of plantar fasciitis, your doctor may recommend you wearing a night splint, which will stretch the arch of your foot and calf while you sleep. This helps to lengthen the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia for symptom relief. Depending on the severity of your plantar fasciitis, your physician may prescribe a store-bought orthotic (arch support) or custom-fitted orthotic to help distribute your foot pressure more evenly.